12 Bald Faced Hornets Facts To Stay Safe
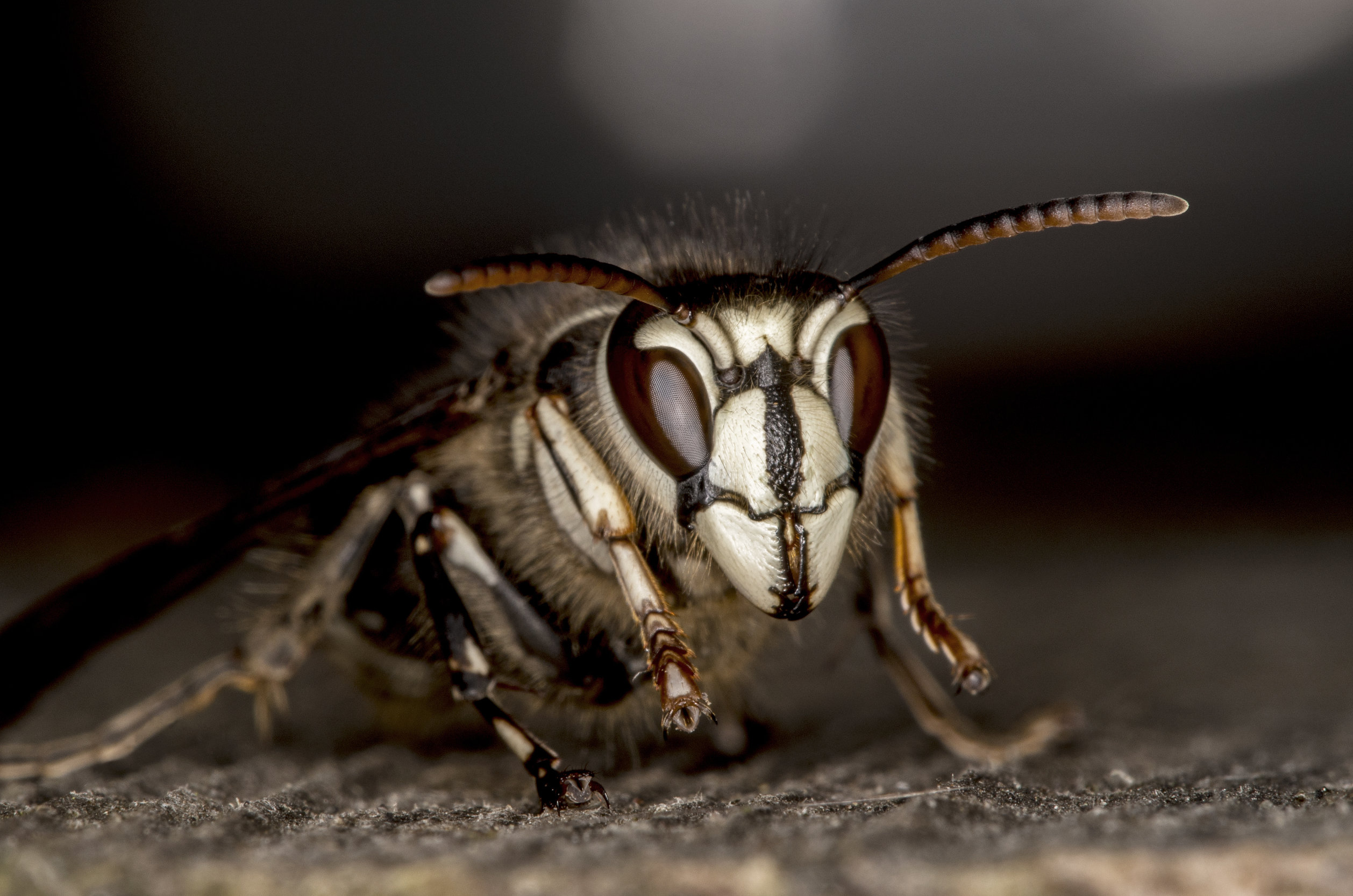

Bald faced hornets are a type of wasp that belongs to the Vespidae family. They are known for their distinctive black and white coloring, as well as their aggressive behavior when threatened or when their nest is disturbed. Here are 12 key facts about bald faced hornets that can help you stay safe:
Identification: Bald faced hornets are typically between 1⁄2 to 5⁄8 inches long, with a black body and a white or pale yellow face. They have a slender waist and a rounded abdomen. Their black and white coloration serves as a warning signal to potential predators, indicating that they are capable of defending themselves.
Habitat: These hornets are commonly found in North America, particularly in the United States and Canada. They tend to build their nests in protected areas such as eaves, attics, and tree cavities. The nests are usually grey or brown in color, papery in texture, and can be quite large, containing thousands of individual hornets.
Diet: Bald faced hornets are primarily carnivorous, feeding on insects, spiders, and other small arthropods. They also consume sugary substances like fruit and tree sap. This diet helps them gather the energy and nutrients needed to build and maintain their complex social structure.
Social Structure: Like other social wasps, bald faced hornets live in colonies with a single queen. The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers (sterile females) forage for food, care for young, and defend the nest. Males, or drones, have only one purpose: to mate with the queen. This social hierarchy is crucial for the survival and success of the colony.
Nesting Behavior: Bald faced hornets are known for their large, exposed nests, which can grow up to 3 feet in diameter. The nest is built from wood pulp and saliva, which hardens into a papery material. The hornets construct the nest in a way that protects it from the elements and potential predators, showcasing their engineering capabilities.
Aggression: Bald faced hornets are highly aggressive when their nest is threatened. They can attack in large numbers, and their venom is powerful enough to cause significant pain and swelling in humans. Unlike honeybees, bald faced hornets can sting repeatedly without harm to themselves, making them a more formidable opponent.
Sting: The sting of a bald faced hornet contains a venom that can cause anaphylaxis in some individuals. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, and a drop in blood pressure. If you suspect you are having an allergic reaction to a hornet sting, seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention: To avoid encounters with bald faced hornets, it’s essential to seal any cracks or crevices around your home, remove standing water, and keep sweet or fermented substances covered. Regularly inspecting your property for signs of hornet activity, such as nests or individual hornets flying around a specific area, can also help prevent unwanted encounters.
Removal: If you find a bald faced hornet nest on your property, do not attempt to remove it yourself. Instead, contact a professional pest control service that has the necessary equipment and expertise to safely remove the nest. Removing a nest without proper precautions can lead to aggressive behavior from the hornets, putting you and others at risk.
Protection: When outdoors, especially during the summer months when hornets are most active, wear protective clothing such as long sleeves, long pants, and a veil to cover your face. Avoid perfumes, colognes, or other fragrances that might attract hornets. If you see a hornet, remain calm and slowly back away. Do not swat at it or make sudden movements, as this can provoke an attack.
First Aid: If you are stung by a bald faced hornet, remove the stinger immediately by scraping it off with your fingernail or a credit card. Do not pinch or squeeze the stinger, as this can release more venom into your skin. Wash the area with soap and water, apply a cold compress to reduce swelling, and take an antihistamine or use a topical cream to alleviate itching and discomfort.
Legal and Environmental Considerations: In many areas, bald faced hornets are considered beneficial insects due to their role in controlling pest populations. As such, there may be regulations against destroying their nests or using certain pesticides. Always check local laws and consider the environmental impact before taking any action against bald faced hornets or their nests. It’s also worth noting that these hornets play a vital role in the ecosystem, serving as both predators and prey for other animals.
By understanding and respecting the nature and behaviors of bald faced hornets, we can coexist with them more safely and appreciate their contributions to our environment. Whether you’re a nature enthusiast, a homeowner, or simply someone who spends time outdoors, being aware of these fascinating creatures can enrich your experience and help you navigate potential encounters with confidence.