5 Key Differences
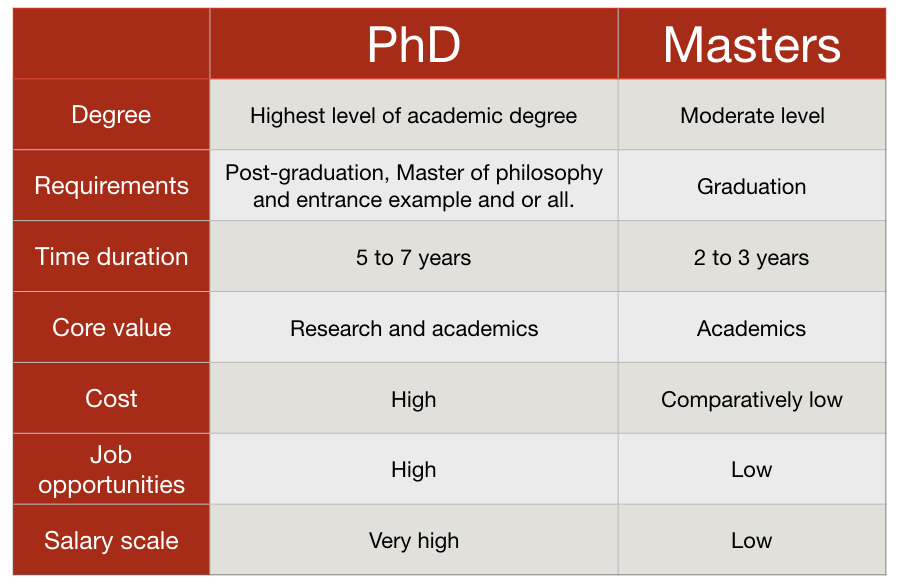
When considering the nuances of various concepts, products, or services, understanding the distinctions between them is crucial for making informed decisions. In this exploration, we will delve into the 5 key differences that set apart two entities, providing a comprehensive overview that not only outlines their unique characteristics but also offers insights into their implications and applications.
1. Fundamental Purpose
The primary purpose of each entity is often the most straightforward difference, yet it underscores the foundational intent behind their creation or development. For instance, if we are comparing two software tools, one might be designed with a focus on user interface simplicity, aiming to make complex tasks more accessible to a broader audience. In contrast, the other might prioritize advanced features and customization options, catering to the needs of professional users. This difference in purpose reflects the distinct values and goals of their respective developers and the targeted user bases.
2. Core Functionality
Beyond the purpose, the core functionality of each entity is another critical differentiator. This aspect refers to the specific tasks or operations that each is designed to perform. Using the software example, one tool might excel in data analysis, providing robust algorithms and models for predictive analytics. The other, however, might focus more on data visualization, offering a wide range of graphs, charts, and other visual tools to help users communicate insights more effectively. The choice between these tools would depend on whether the user’s primary need is to analyze data or to present findings.
3. Operational Efficiency
The operational efficiency of an entity refers to how effectively it uses resources to achieve its intended purpose. This can include factors such as speed, memory usage, ease of use, and scalability. For example, in comparing two types of renewable energy systems, solar panels might offer higher efficiency in terms of energy conversion rates under optimal conditions, while wind turbines might provide more consistent power output over a broader range of environmental conditions. Understanding these efficiencies is crucial for selecting the best fit for specific scenarios or applications.
4. User Experience
The user experience (UX) encompasses all aspects of the end-user’s interaction with an entity, including how it makes them feel, how easy it is to use, and the overall sense of satisfaction derived from the interaction. Differences in UX can significantly influence user adoption and loyalty. For instance, a smartphone with an intuitive interface, seamless app integration, and personalized features might offer a superior UX compared to a competitor’s model that, while offering similar technical specifications, lacks in usability and customization options. The perception of value and brand loyalty often stem from these UX differences.
5. Adaptability and Scalability
Finally, the adaptability and scalability of an entity are vital for its long-term relevance and effectiveness. This refers to its ability to evolve with changing user needs, technological advancements, and environmental conditions. In the context of business strategies, for example, one approach might prioritize flexibility and rapid response to market changes, while another focuses on building a robust, scalable infrastructure that can support significant growth. The choice between these strategies depends on the company’s industry, resources, and growth goals, highlighting the importance of aligning an entity’s characteristics with its operational environment and objectives.
In conclusion, understanding the 5 key differences between entities, whether they are products, services, concepts, or strategies, provides a nuanced perspective that can guide decision-making, foster innovation, and optimize outcomes. By examining purpose, functionality, efficiency, user experience, and adaptability, individuals and organizations can make informed choices that align with their needs, values, and goals, ultimately leading to greater success and satisfaction.
What is the primary factor to consider when evaluating the differences between entities?
+The primary factor often depends on the context and purpose of the evaluation. However, understanding the fundamental purpose and core functionality of each entity provides a foundational basis for comparison.
How does the operational efficiency of an entity impact its effectiveness?
+The operational efficiency of an entity directly affects its ability to achieve its intended goals while minimizing waste and optimizing resource use. High efficiency can lead to better outcomes, cost savings, and increased user satisfaction.
What role does user experience play in the adoption and loyalty towards an entity?
+User experience is crucial as it influences how users perceive an entity's value, ease of use, and overall satisfaction. A superior UX can significantly increase adoption rates and foster long-term loyalty.
In the realm of decision-making, whether personal or professional, recognizing and understanding these differences is not merely about making distinctions but about aligning choices with specific needs, preferences, and objectives. As entities evolve and new options emerge, the ability to discern and appreciate these nuances becomes increasingly valuable, enabling more informed, effective, and satisfying interactions with the world around us.

