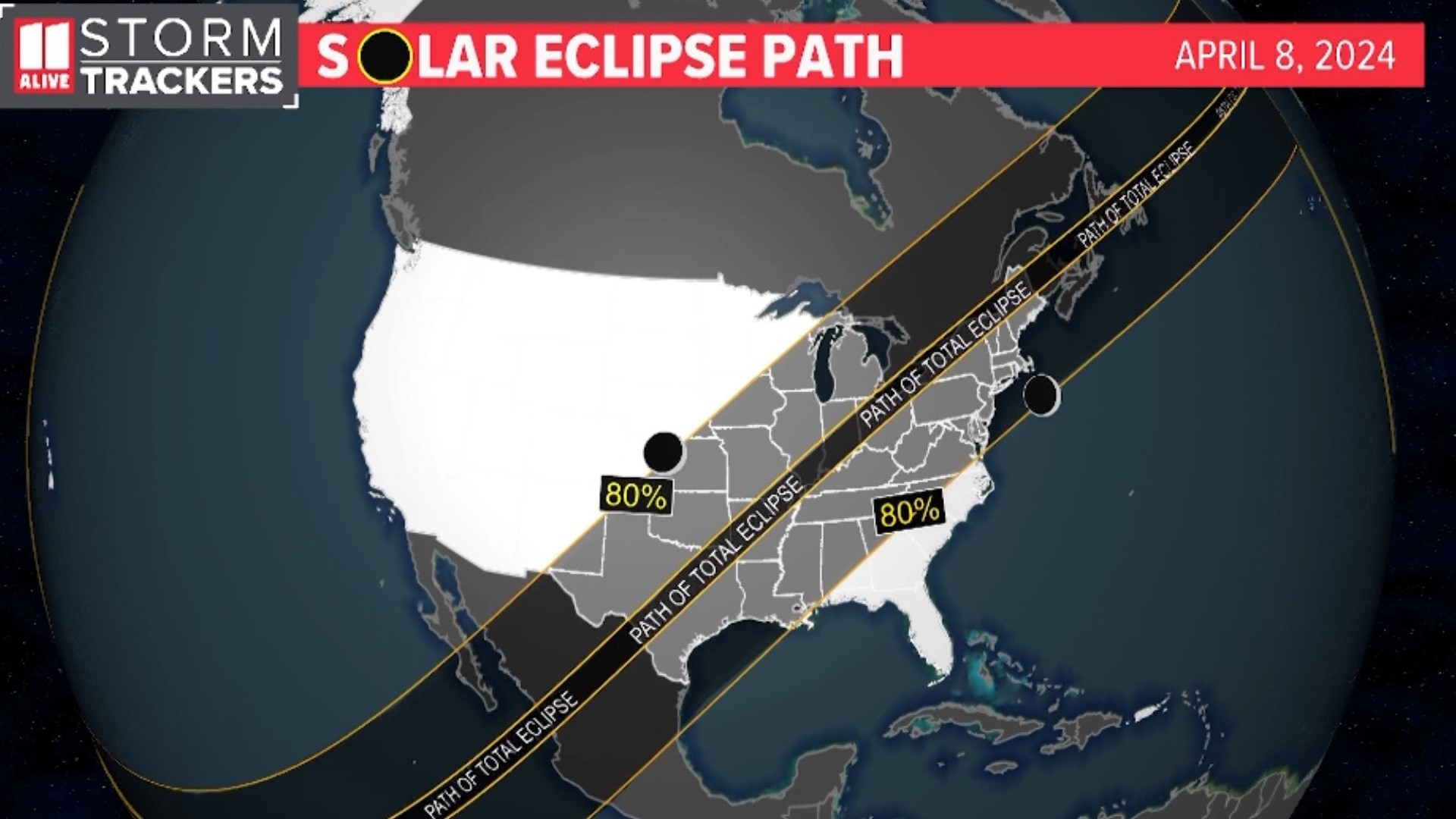
Sequence Essentials: Mastering Event Order
When it comes to understanding and analyzing complex systems, sequences, and events, the concept of sequence essentials emerges as a fundamental principle. Sequence essentials refer to the critical components and rules that govern the order of events, actions, or tasks within a process or system. Mastering sequence essentials is crucial for ensuring efficiency, effectiveness, and reliability in various domains, from project management and programming to logistics and manufacturing.
To delve into the realm of sequence essentials, it is essential to first comprehend the basic principles of sequencing. Sequencing involves arranging items, tasks, or events in a specific order, which is often determined by dependencies, priorities, or logical constraints. In many cases, the order of events can significantly impact the outcome, performance, or safety of a system or process. For instance, in a manufacturing line, the sequence of operations can affect product quality, production time, and resource allocation.
One of the primary sequence essentials is understanding the dependencies between events or tasks. Dependencies can be categorized into different types, including:
- Precedence constraints: These dictate that one task must be completed before another can start. For example, in a construction project, the foundation must be laid before the walls can be built.
- Resource dependencies: These occur when tasks require the same resource, such as a machine or a skilled worker, and thus cannot be performed simultaneously.
- Temporal dependencies: These involve time-based relationships between tasks, such as a task that must be completed within a certain timeframe after another task has started.
Effective management of these dependencies is vital for creating an efficient sequence of events. This involves identifying critical path tasks, which are those tasks that determine the minimum duration required to complete the project, and managing resources to ensure that no bottlenecks occur.
Another crucial aspect of sequence essentials is prioritization. When multiple tasks or events are competing for resources or time, prioritization determines which should be addressed first. Prioritization criteria can include urgency, importance, complexity, and the impact of delaying a task. For example, in a software development project, fixing critical bugs might take priority over implementing new features to ensure the stability and security of the system.
The sequencing of events can also be influenced by external factors such as environmental conditions, regulatory requirements, and stakeholder expectations. For instance, in agriculture, the sequence of planting, irrigation, and harvesting is heavily dependent on weather conditions and seasonal changes. Similarly, in the aviation industry, the sequence of flight preparations, takeoff, and landing must comply with strict safety protocols and regulatory guidelines.
In addition to understanding dependencies and prioritization, mastering sequence essentials involves leveraging various sequencing techniques and tools. These can range from simple methods like the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) and the Critical Path Method (CPM) to more complex algorithms and software solutions designed for scheduling and resource allocation.
Moreover, sequence essentials play a significant role in ensuring the adaptability and resilience of systems and processes. In dynamic environments where unexpected changes or disruptions can occur, the ability to resequence events or tasks quickly can be critical. This might involve having contingency plans, maintaining flexible resource allocations, and continuously monitoring the sequence of events to identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
In conclusion, sequence essentials represent a fundamental set of principles and practices that are indispensable for managing complex sequences of events, tasks, or actions. By fully grasping these essentials, including dependencies, prioritization, external factors, sequencing techniques, and adaptability, individuals and organizations can significantly enhance the efficiency, reliability, and performance of their systems and processes.
Practical Applications of Sequence Essentials
The application of sequence essentials is vast and varied, touching upon numerous aspects of personal and professional life. Here are a few examples:
- Project Management: In managing projects, understanding sequence essentials helps in creating realistic timelines, allocating resources effectively, and managing dependencies to ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget.
- Manufacturing and Logistics: Sequencing production tasks and supply chain operations can optimize production efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality.
- Software Development: Developers use sequence essentials to manage the development process, prioritize features, and ensure that software releases meet quality and functionality standards.
- Personal Productivity: Applying sequence essentials to daily tasks and goals can help individuals prioritize their time more effectively, manage their workload, and achieve a better work-life balance.
Best Practices for Implementing Sequence Essentials
- Detailed Planning: Start with a thorough analysis of tasks, dependencies, and resources to create a comprehensive plan.
- Flexibility: Build flexibility into your plans to accommodate unexpected changes or setbacks.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly review the sequence of events to identify inefficiencies or potential bottlenecks.
- Communication: Ensure that all stakeholders are informed about the sequence of events and any changes that may occur.
- Adaptability: Be prepared to adjust the sequence as needed based on new information, changes in priorities, or external factors.
The Future of Sequence Essentials
As technology continues to evolve, particularly with advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT), the management of sequence essentials is likely to become even more sophisticated. Automated sequencing tools will be able to analyze complex systems, predict potential bottlenecks, and optimize sequences in real-time, leading to increased efficiency and productivity across various industries.
Furthermore, the integration of sequence essentials with emerging technologies like blockchain can enhance transparency, security, and reliability in sequencing processes, especially in areas such as supply chain management and financial transactions.
In the realm of project management and personal productivity, AI-driven tools will assist in creating personalized sequence plans, predicting task durations, and automating routine decisions, freeing up human resources for more strategic and creative endeavors.
As we move forward, understanding and mastering sequence essentials will remain a critical skill for both individuals and organizations seeking to navigate the complexities of modern systems and processes effectively.
What are the primary factors to consider when sequencing events or tasks?
+The primary factors include dependencies between tasks, resource availability, temporal constraints, and prioritization based on urgency, importance, and complexity.
How can sequence essentials be applied in personal productivity?
+Applying sequence essentials to daily tasks and goals involves prioritizing tasks based on importance and urgency, managing time effectively, and minimizing distractions to achieve a better work-life balance.
What role does technology play in managing sequence essentials?
+Technology, especially advanced tools and software, plays a significant role in analyzing complex systems, predicting potential issues, optimizing sequences, and automating decisions, thereby increasing efficiency and productivity.